Rational numbers worksheets Grade 6
Rational numbers worksheets Grade 6

- INTRODUCTION
- Download worksheets
- Related Contents
- Understanding types of rational numbers worksheets Grade 6:...
Get more contents on Rational numbers activities for Grade 6 with answers...
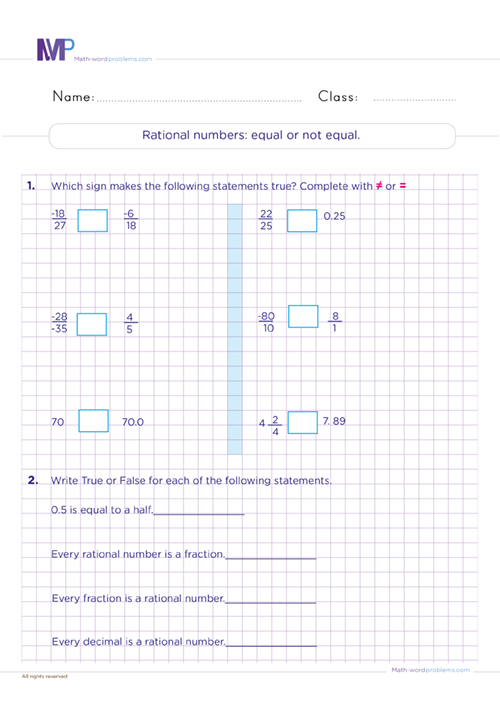
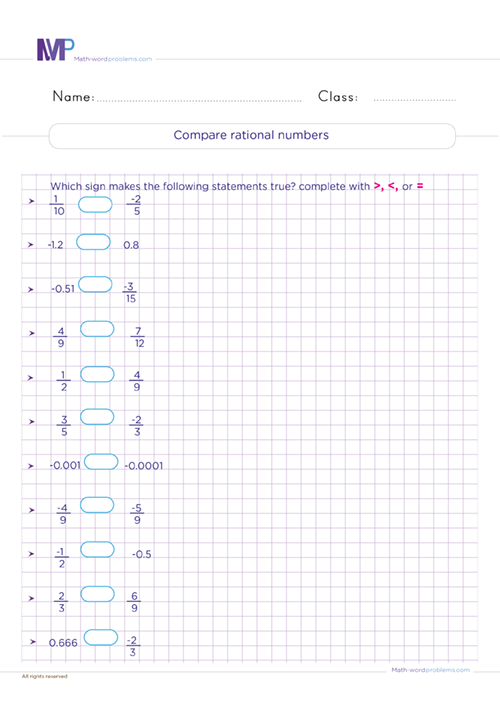
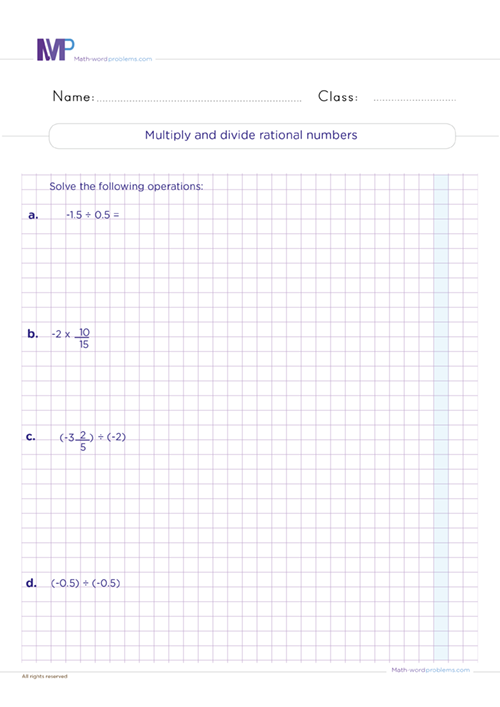
Get the best practice for comparing and ordering rational numbers worksheets Grade 6. 6th graders will learn how to find the absolute value, add, subtract, multiply, divide, compare, and order different rational types of rational numbers using simple and fun strategies. Note that multiplication and division of rational numbers are done the same way as fractions.
As we know, there are many quantities or measures that integers alone cannot adequately describe. For instance, an integer can simply be written as 5. Whereas we express rational numbers as the ratio of two integers, such as 5/1 or 5:1. However, all integers, common fractions, negative and positive numbers/fractions, mixed numbers, and finite or repeating decimals are rational numbers. We commonly use them when measuring quantities, whether length, mass, time, etc.
While solving these fantastic rational numbers worksheets, your 6th graders will understand all the different types of numbers, which is a foundational stone to many other math areas, like algebra.
Absolute value worksheet Grade 6 with answers
Your 6th graders will have an enjoyable time while solving our thrilling absolute value worksheet Grade 6 with answers. Hopefully, you can bear with us that numbers are placed on a number line beginning with zero and moving to the right (positive numbers) and left (negative numbers). So, an absolute value is how far a number is from zero, whether negative or positive. Given this, our rational numbers worksheets Grade 6 will illustrate and help you learn why a number stays the same when you have opposite integers with and without using number lines.
The symbol for absolute value looks like two short vertical lines, "//." The simplest way to solidify kids' mastery of the absolute value concept is by enabling them to -5 and 5 are all 5 spaces away from zero. Hence, the absolute value of both positive and negative numbers will always be the positive version of that number. For instance;
|7| = 7
|-7| = 7
As you can see, this is a fantastic mental skill that you can solve without even using a number line. With an accurate mastery of finding absolute values, your kids can now dive into comparing and ordering rational numbers worksheets and many other rational numbers exercises.
Of equal importance in this resource, we hope to strengthen kid's skills in comparing and understanding numbers by designing different methods of ordering rational numbers, i.e., from least to greatest and vice versa. Besides, comparing rational numbers is equally an ideal way to enhance kids' converting fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers.
Understanding types of rational numbers worksheets Grade 6: Natural numbers, Whole numbers, Integers, Fractions, Terminating decimals, Non-terminating decimals
A perfect way to enhance kids' understanding types of rational numbers worksheets Grade 6: Natural numbers, Whole numbers, Integers, Fractions, Terminating decimals, and Non-terminating decimals is by giving a brief description of each type.
-
Rational numbers are written as a ratio of two integers. For example, 4/5, -5/2, and 0.6 are all rational numbers. We can classify rational numbers into different types based on their properties. Our worksheets consist of exercises of each type for perfect practice and mastery.
-
Integers are all whole numbers along with their negative counterparts. For example, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ... are all integers. Integers can also be written as fractions with a denominator of 1. For example, -4 = -4/1.
-
Fractions: Fractions are numbers written as a ratio of two integers where the denominator is not zero. For example, 3/4, -7/3, and 5/7 are all fractions.
-
Terminating decimals have a finite number of digits after the decimal point. For example, 0.75, -1.5, and 2.6 are all terminating decimals.
-
Non-terminating decimals have an infinite number of digits after the decimal point that does not repeat in a pattern. For example, √2 = 1.41421356237..., π = 3.14159265359..., and e = 2.71828182846... are all non-terminating decimals. Non-terminating decimals cannot be written as fractions because they are irrational numbers.
As your kids enjoy practicing these rational numbers exercises, they'll grab the following skills: Characteristics of rational numbers, identifying rational numbers, comparing and ordering rational numbers from least to greatest.